DRAG DROP
You are developer for a Microsoft Azure SQL Database instance.
You are creating a new stored procedure. The procedure must perform the following tasks in this order: -1. Update a table named OrderHistory. -2. Delete rows from a table named Orders. -3. Delete rows from a table named Customers. -4. Insert rows into a table named ProcessHistory.
You need to ensure that the procedure meets the following requirements:
-If either DELETE operation fails, the rest of operation must continue. -If either the UPDATE operation or the INSERT operation fails, the whole procedure should fail and no changes should be retained.
Which four Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate Transact-SQL segments from the list of Transact-SQL segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.

Answer: 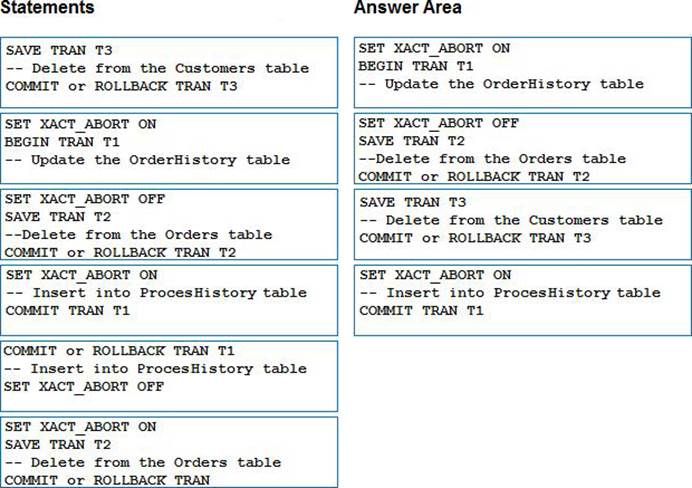
Explanation:
When SET XACT_ABORT is ON, if a Transact-SQL statement raises a run-time error, the entire transaction is terminated and rolled back.
When SET XACT_ABORT is OFF, in some cases only the Transact-SQL statement that raised the error is rolled back and the transaction continues processing.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/set-xact-abort-transactsql?view=sql-server-2017
