A company has a two-tier application architecture that runs in public and private subnets Amazon EC2 instances running the web application are in the public subnet and a database runs on the private subnet. The web application instances and the database are running in a single Availability Zone (AZ).
Which combination of steps should a solutions architect take to provide high availability for this architecture? (Select TWO.)
A . Create new public and private subnets in the same AZ for high availability
B . Create an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group and Application Load Balancer spanning multiple AZs
C . Add the existing web application instances to an Auto Scaling group behind an Application Load Balancer
D . Create new public and private subnets in a new AZ Create a database using Amazon EC2 in one AZ
E . Create new public and private subnets in the same VPC each in a new AZ Migrate the database to an Amazon RDS multi-AZ deployment
Answer: B, E
Explanation:
You can take advantage of the safety and reliability of geographic redundancy by spanning your Auto Scaling group across multiple Availability Zones within a Region and then attaching a load balancer to distribute incoming traffic across those zones. Incoming traffic is distributed equally across all Availability Zones enabled for your load balancer.
Note
An Auto Scaling group can contain Amazon EC2 instances from multiple Availability Zones within the same Region. However, an Auto Scaling group can’t contain instances from multiple Regions.
When one Availability Zone becomes unhealthy or unavailable, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling launches new instances in an unaffected zone. When the unhealthy Availability Zone returns to a healthy state, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling automatically redistributes the application instances evenly across all of the zones for your Auto Scaling group. Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling does this by attempting to launch new instances in the Availability Zone with the fewest instances. If the attempt fails, however, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling attempts to launch in other Availability Zones until it succeeds.
You can expand the availability of your scaled and load-balanced application by adding an Availability Zone to your Auto Scaling group and then enabling that zone for your load balancer. After you’ve enabled the new Availability Zone, the load balancer begins to route traffic equally among all the enabled zones.
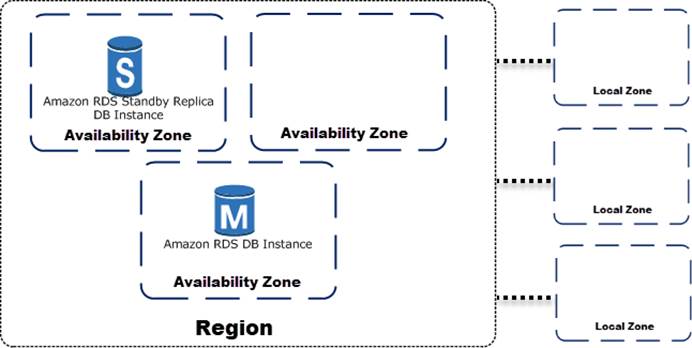
High Availability (Multi-AZ) for Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS provides high availability and failover support for DB instances using Multi-AZ deployments. Amazon RDS uses several different technologies to provide failover support. Multi-AZ deployments for MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL DB instances use Amazon’s failover technology. SQL Server DB instances use SQL Server Database Mirroring (DBM) or Always On Availability Groups (AGs).
In a Multi-AZ deployment, Amazon RDS automatically provisions and maintains a synchronous standby replica in a different Availability Zone. The primary DB instance is synchronously replicated across Availability Zones to a standby replica to provide data redundancy, eliminate I/O freezes, and minimize latency spikes during system backups. Running a DB instance with high availability can enhance availability during planned system maintenance, and help protect your databases against DB instance failure and Availability Zone disruption. For more information on Availability Zones, see Regions, Availability Zones, and Local Zones
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/userguide/as-add-availability-zone.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/Concepts.MultiAZ.html
