A company is hosting a web application on AWS using a single Amazon EC2 instance that stores user-uploaded documents in an Amazon EBS volume For better scalability and availability the company duplicated the architecture and created a second EC2 instance and EBS volume in another Availability Zone: placing both behind an Application Load Balancer After completing this change users reported that each time they refreshed the website they could see one subset of their documents or the other but never all of the documents at the same time
What should a solutions architect propose to ensure users see all of their documents at once?
A . Copy the data so both EBS volumes contain all the documents
B . Configure the Application Load Balancer to direct a user to the server with the documents
C . Copy the data from both EBS volumes to Amazon EFS Modify the application to save new documents to Amazon EFS
D . Configure the Application Load Balancer to send the request to both servers Return each document from the correct server
Answer: C
Explanation:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/efs/latest/ug/how-it-works.html#how-it-works-ec2
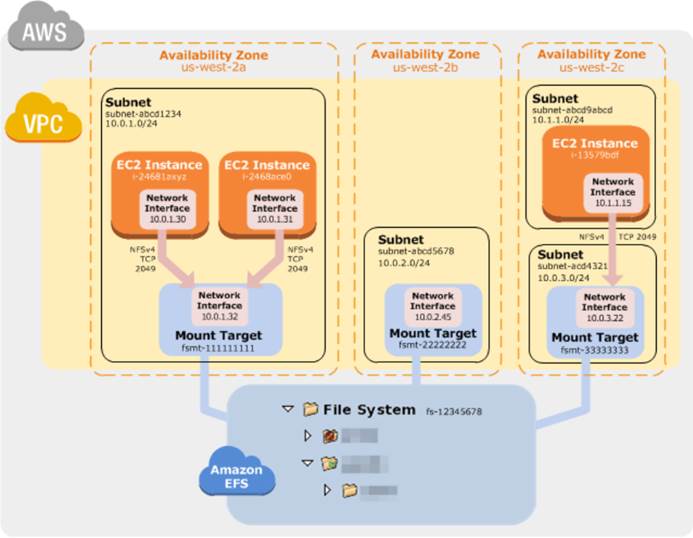
Amazon EFS provides file storage in the AWS Cloud. With Amazon EFS, you can create a file system, mount the file system on an Amazon EC2 instance, and then read and write data to and from your file system. You can mount an Amazon EFS file system in your VPC, through the Network File System versions 4.0 and 4.1 (NFSv4) protocol. We recommend using a current generation Linux NFSv4.1 client, such as those found in the latest Amazon Linux, Redhat, and Ubuntu AMIs, in conjunction with the Amazon EFS Mount Helper. For instructions, see Using the amazon-efs-utils Tools.
For a list of Amazon EC2 Linux Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) that support this protocol, see NFS Support. For some AMIs, you’ll need to install an NFS client to mount your file system on your Amazon EC2 instance. For instructions, see Installing the NFS Client.
You can access your Amazon EFS file system concurrently from multiple NFS clients, so applications that scale beyond a single connection can access a file system. Amazon EC2 instances running in multiple Availability Zones within the same AWS Region can access the file system, so that many users can access and share a common data source.
How Amazon EFS Works with Amazon EC2
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/efs/latest/ug/how-it-works.html#how-it-works-ec2