HOTSPOT
A company plans to use Azure SQL Database to support a line of business application. The application will manage sensitive employee data.
The solution must meet the following requirements:
– Encryption must be performed by the application.
– Only the client application must have access keys for encrypting and decrypting data.
– Data must never appear as plain text in the database.
– The strongest possible encryption method must be used.
– Searching must be possible on selected data.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Answer: 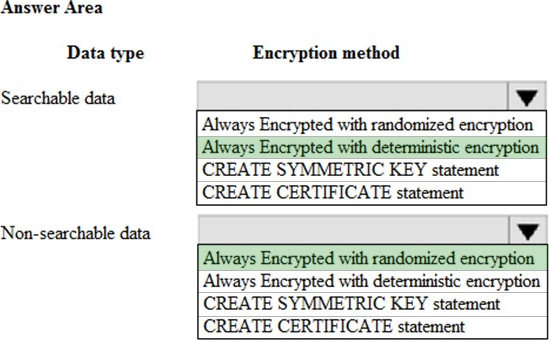
Explanation:
Box 1: Always Encrypted with deterministic encryption
Deterministic encryption always generates the same encrypted value for any given plain text value. Using deterministic encryption allows point lookups, equality joins, grouping and indexing on encrypted columns.
However, it may also allow unauthorized users to guess information about encrypted values by examining patterns in the encrypted column, especially if there is a small set of possible encrypted values, such as True/False, or North/South/East/West region. Deterministic encryption must use a column collation with a binary2 sort order for character columns.
Box 2: Always Encrypted with Randomized encryption
– Randomized encryption uses a method that encrypts data in a less predictable manner. Randomized
encryption is more secure, but prevents searching, grouping, indexing, and joining on encrypted
columns.
Note: With Always Encrypted the Database Engine never operates on plaintext data stored in encrypted columns, but it still supports some queries on encrypted data, depending on the encryption type for the column. Always Encrypted supports two types of encryption: randomized encryption and deterministic encryption.
Use deterministic encryption for columns that will be used as search or grouping parameters, for example a government ID number. Use randomized encryption, for data such as confidential investigation comments, which are not grouped with other records and are not used to join tables.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/encryption/always-encrypted-databaseengine

Leave a Reply